 |
|
|
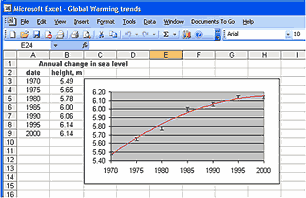
Students need to appreciate that scientific theories must be supported by evidence. But what is evidence? Evidence is usually considered to be data from survey or experiment or previous research. However, realistically it relates to more than just hard facts. It embraces the results of analyses and consultations and so includes opinions, judgments and beliefs. The experimenter effect is well known when scientists interpret their results. The evidence base for a theory is not static; it changes constantly as scientist's understanding changes and as new research results come in. When the evidence isn’t clear-cut, scientists will assign a level of confidence to their prediction from the data. You can read more about this in Understanding the Maths ModellingEvidence collected by scientists is also used to create models of processes in order to understand them and to be able to make predictions. However these models have limitations. They are often simplifications, and it is difficult to generalise from one model developed using data in one context to another context.
|



What's your opinion?
Average rating




Not yet rated